- Qinsun Instruments Co., Ltd.
- Tell:+86-21-6780 0179
- Phone:+86-17740808215
- Address:No. 2578 Minhang District Gu Dai Road, Shanghai
- Contact:Mr. Li
- QQ:846490659
What factors can affect the scratch resistance of a material or surface?
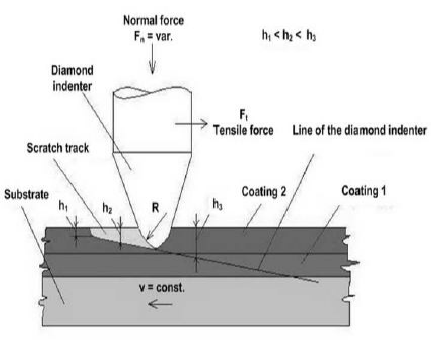
There are several factors that may affect the scratch resistance of a material or surface, these include:
1. Material hardness: In general, harder materials tend to have better scratch resistance. The hardness of a material can be measured quantitatively by various methods, such as the Rockwell Hardness Test or the Vickers Hardness Test.
2. Surface coatings or protective layers: Materials that are coated with abrasion-resistant paints, lacquers, coatings, or other protective layers generally have better scratch resistance. These coatings provide additional protection and mitigate the effects of scratches on the base material.
3. Surface quality: Surfaces that are smooth, uniform and free of visible defects generally have better scratch resistance. Surface defects, such as particles, pits or grooves, tend to be the starting and expansion points for scratches.
4. Material structure: The structure and organization of a material can also have an effect on scratch resistance. For example, materials with a tighter structure and higher fiber or grain orientation generally have better scratch resistance.

5. Scratch force and speed: The scratch force and speed applied to the surface of a material also have an effect on its scratch resistance. Higher scratching force and speed may result in more severe scratches. 6.
6. External Environmental Factors: Environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity and the presence of chemicals, may also have an effect on the scratch resistance of a material. In some special environments, the scratch resistance of the material may be reduced.
Please note that the above factors and their effects vary depending on the type of material and application. When conducting scratch resistance tests or selecting materials, these factors should be taken into account and the appropriate material or coating should be selected for the specific need.
What are the common methods for scratch resistance testing?
Common methods for testing the scratch resistance of materials include the following:
1. Scratch testing: A scratch test is performed on a material using a scratch tester. Scratch testing usually involves applying a scratching tool with a certain load to the surface of the material, and then evaluating the scratch resistance based on the depth, length or other characteristics of the scratch.
2. Hardness testing: The scratch resistance of a material is indirectly assessed by performing a hardness test on the surface of the material, for example, using a Rockwell or Brinell hardness tester. Higher hardness values are usually associated with better scratch resistance. 3.
3. Abrasion tests: Abrasion tests can be used to assess the scratch resistance of a material. These tests typically involve the application of friction, sliding or reciprocating motion to the surface of the material to simulate wear under actual conditions of use, and the degree of wear is used to assess the scratch resistance of the material.
4. Needle Tip Test: A scratch or puncture test is performed on the surface of a material using the tip of a needle or other sharp object to evaluate the scratch resistance of the material. This test method is often used to evaluate the scratch resistance of films, coatings or flexible materials.
5. Fingernail Test: This is a simple method of assessing the scratch resistance of a material by applying force to the surface of the material with a fingernail or fingertip. However, this method is more subjective and results may not be sufficiently accurate and repeatable.
The choice of these methods depends on the specific application and requirements. Prior to performing a scratch resistance test, it is recommended to consult applicable standards or specifications and select the appropriate test method for the particular material and application.





