- Qinsun Instruments Co., Ltd.
- Tell:+86-21-6780 0179
- Phone:+86-17740808215
- Address:No. 2578 Minhang District Gu Dai Road, Shanghai
- Contact:Mr. Li
- QQ:846490659
What is the air permeability test ASTM D737?
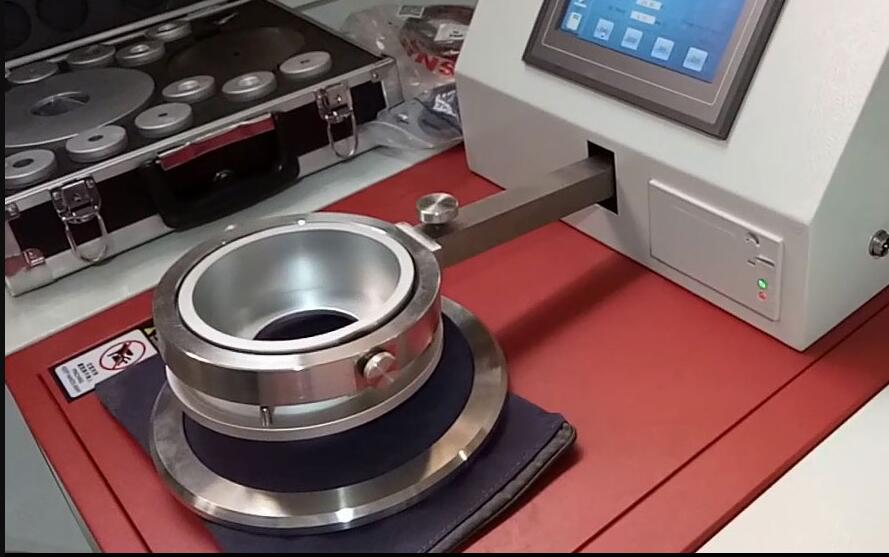

ASTM D737 is a standard test method established by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) to measure the air permeability of textile fabrics. Air permeability is an important property that determines the breathability and comfort of fabrics in various applications, such as apparel, medical textiles, and filtration materials.
The test method outlined in ASTM D737 provides a quantitative measurement of the airflow through a fabric under specified test conditions. It helps in assessing the suitability of a fabric for specific applications where air exchange or ventilation is essential.

Here is a detailed explanation of the ASTM D737 test method:
1. Test Apparatus:
- Air Permeability Test Instrument: A testing apparatus equipped with a suitable device to generate a constant airflow through the fabric sample.
- Test Head: A circular test head with a known area, usually 38.6 cm² (6 square inches) with an opening at the center that allows the fabric to be clamped.
- Differential Pressure Gauge: A gauge that measures the pressure drop across the fabric during the test.
- Stopwatch or Timer: Used to measure the test duration accurately.
2. Sample Preparation:
- Cut specimens: Cut circular specimens with a diameter of about 11.2 cm (4.4 inches) from the fabric using a suitable template.
- Conditioning: Condition the test specimens at standard atmospheric conditions of 20 ± 2°C (68 ± 4°F) and 65 ± 4% relative humidity for a minimum of four hours before testing.
3. Test Procedure:
- Mount the fabric specimen: Place the conditioned fabric specimen on the test head, ensuring that it is flat and free from folds or creases. Clamp the specimen securely to cover the opening completely.
- Measure the test apparatus: Verify that the air permeability test instrument and the differential pressure gauge are calibrated and functioning correctly.
- Adjust the airflow: Set the airflow rate to 4.9 cm³/s/cm² (200 ft³/ft²/min) by adjusting the appropriate controls on the testing equipment.
- Record the initial pressure: Record the initial differential pressure reading on the gauge and start the stopwatch or timer.
- Test duration: Measure the time duration over which the differential pressure is measured. The test duration is typically 1 minute.
- Record the final pressure: After the test duration, record the final differential pressure reading.
- Calculate the air permeability: Calculate the air permeability of the fabric using the formula provided in the ASTM standard. Air permeability is expressed in units of cubic centimeters per second per square centimeter (cm³/s/cm²) or cubic feet per minute per square foot (ft³/ft²/min).
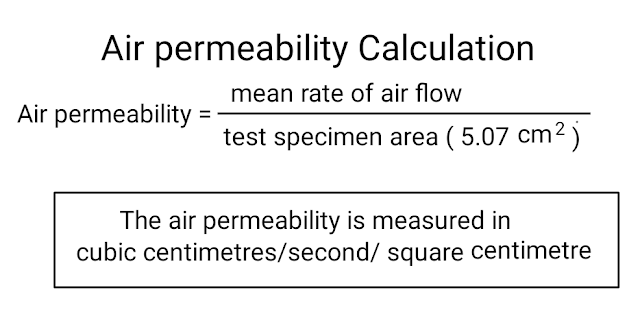
4. Calculation:
The air permeability (K) is calculated using the formula:
K = ΔP × V / A
Where:
K = Air permeability (cm³/s/cm² or ft³/ft²/min)
ΔP = Differential pressure (Pa or in. water column)
A = Test head area (cm² or in²)
V = Airflow rate (cm³/s or ft³/min)
5. Reporting:
Report the air permeability results along with the details of the fabric tested, including fabric type, sample conditioning, and any deviations from the test procedure.
The ASTM D737 test method provides a standardized and reproducible way of measuring the air permeability of textile fabrics. It enables manufacturers, researchers, and quality control personnel to evaluate fabric performance and compare it with specific application requirements. The results obtained from this test method help in the development and selection of fabrics suited for diverse end-uses, including clothing, accessories, and functional textiles.
It is important to note that this explanation provides a general overview of the ASTM D737 test method. For detailed and accurate testing, it is essential to refer directly to the ASTM standard and follow the specific guidelines and requirements outlined therein. Additionally, testing laboratories and manufacturers may have their own equipment and variations of the test method, while still conforming to the ASTM standard.





